Idea Description
Advancing Energy Solutions: Nuclear Power in a Sustainable Future
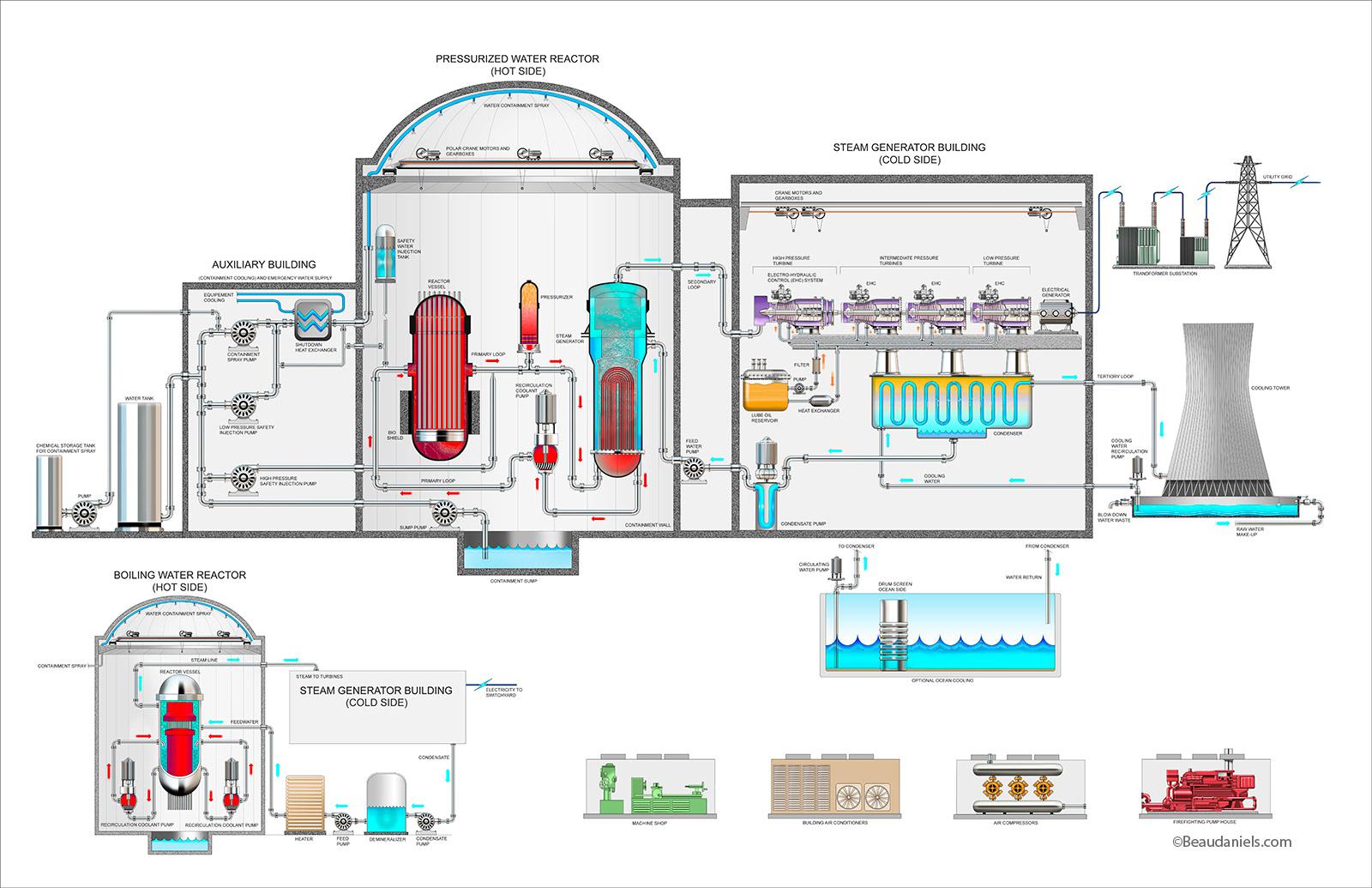
Nuclear power relies on a process called Nuclear fission. This is the process of heavier nuclei, such as uranium, being split up into lighter nuclei and neutrons. When given enough energy to do so, usually by firing a slow-moving neutron at a radioactive nucleus, the nuclei will split into constituents which include an amount of lighter nuclei, and two or more neutrons. The production of extra neutrons is important, as only one neutron is required to produce a nuclear fission reaction. (this means that a chain reaction is set up, as more and more neutrons are produced to ignite further fission reactions which then produce even more neutrons). When a nuclear fission reaction takes place, a LOT of energy is released. This can be represented via Einstein's famous equation: E = mc2
Why nuclear energy is better than fossil fuels
Transitioning away from fossil fuels is central to efforts to curtail climate change, clean up the air, and slow biodiversity loss. A side-by-side comparison reveals that nuclear power is far better than fossil fuels. According to the Center for Climate and Energy Solutions, coal plants generate around 2,200 lbs of carbon pollution per megawatt-hour (MWh), natural gas generates 1,100 lbs of CO2 per MWh while nuclear does not generate any. The overwhelming logic of nuclear power is impossible to ignore.
Nuclear energy has averted millions of tons of carbon pollution. This is energy that would otherwise have been generated by fossil fuels. Each year more than 470 million metric tons of CO2 emissions are avoided by nuclear power in the U.S. alone. That is equivalent to taking nearly 100 million combustion engines off the road. According to the World Nuclear Association
Nuclear energy is a central part of our efforts to transition away from fossil fuels. As reported by Real Clear Energy, “We have more and more member states recognizing that, in order to achieve the decarbonization goals, we need nuclear in the mix,” an EU industry representative was quoted as saying. Speaking about the energy crisis caused by Russia’s war, the same representative also said, “I think more and more people are starting to recognize the risk of depending on imports”. Russia’s war of choice in Ukraine adds to the rationale for supporting nuclear power. As reported by the Economist, the effort to transition away from Russian fossil fuels is making nuclear energy increasingly attractive.
Advantages of nuclear power compared to renewable energy
Nuclear energy has advantages over renewables in terms of reliability, GHG emissions, land use, and waste. Nuclear is far more reliable (dispatchable) than renewables like wind and solar. Nuclear plants keep churning out energy even when the wind is not blowing, and the sun is not shining.
Nuclear is also one of the cleanest sources of energy. Recent research published in the Journal of Cleaner Production found that the emission of GHGs and natural resource use associated with nuclear power generation was similar to that of renewable energy. An analysis by the European Commission indicates that in terms of full-cycle production, the emissions from nuclear are around the same as wind. Other studies have concluded that nuclear power may be even cleaner than solar.
Economic benefits:
Nuclear energy has several economic advantages over other forms of energy, including its low operating costs, its ability to provide stable and reliable baseload power, and its minimal greenhouse gas emissions.
1. Low Operating Costs in the Long Run: Nuclear power plants, once built and set up, can have relatively low operating costs compared to other forms of energy. This is due to their high capacity factors and low fuel requirements. The average operating cost of a nuclear power plant in the United States in 2020 was 2.14 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh), which is lower than coal-fired (6.81 cents/kWh) and natural gas-fired (3.27 cents/kWh) power plants.
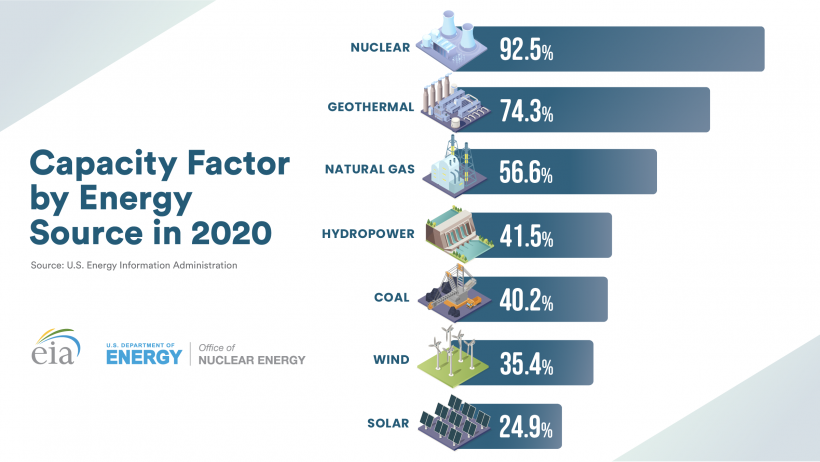
2. Stable and Reliable Baseload Power: Nuclear power plants are well-suited for providing stable and reliable baseload power, meeting the minimum level of electricity demand around the clock. Unlike some other renewable energy sources dependent on weather conditions, nuclear power plants can operate continuously for long periods. They have an average capacity factor of around 80%, which is much higher than wind power (around 25%) and solar power (15-20%).
3. Minimal Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Nuclear energy emits minimal greenhouse gasses compared to fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. With only around 12 grams of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity generated, it is significantly lower than coal-fired (820 grams CO2e/kWh) and natural gas-fired (490 grams CO2e/kWh) power plants.
4. Safety Improvements: Modern nuclear power plants are safer and more secure than older designs. Stringent regulations and oversight from organizations like the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) help ensure the safety of nuclear facilities. With hundreds of operating nuclear power plants worldwide, the track record shows that nuclear energy is becoming safer.
5. Job Creation and Economic Growth: The nuclear energy industry contributes significantly to job creation and economic growth. In the U.S., it supports approximately 475,000 jobs and contributes around $60 billion to the economy each year, as per the Nuclear Energy Institute.
While these are indeed significant advantages of nuclear energy, it's essential to acknowledge that there are also challenges and concerns associated with this energy source. These may include issues of radioactive waste management, high initial construction costs, public perception and acceptance, and the potential for nuclear accidents (though the risk has been significantly reduced through improved safety measures). As with any energy source, it's essential to weigh the benefits and drawbacks to make informed decisions about our energy mix and future sustainability goals.
Nuclear waste danger
Radioactive waste poses a significant environmental and health risk due to its radioactivity, but it will naturally decay over time, becoming less hazardous. The decay process involves unstable atomic nuclei emitting radiation, transforming into more stable forms. This decay rate is measured by the material's half-life, varying from hours to hundreds of thousands of years, depending on the specific radioactive isotopes involved.
Proper management of radioactive waste is crucial to ensure safety during the decay process. Specialized containment and storage facilities are employed to isolate waste from the environment and prevent potential harm to living organisms. Regulatory agencies establish guidelines and protocols for the safe handling and disposal of radioactive waste, prioritizing long-term safety. By adhering to these measures, we can mitigate the risks associated with radioactive waste and protect both current and future generations from its potential adverse effects.
Oman vision 2040 on renewable energy
Oman's future in renewable energy looks promising and environmentally conscious, with ambitious targets to produce renewable hydrogen. By aiming for 1 million tons annually by 2030, 3.75 million tons by 2040, and 8.5 million tons by 2050, surpassing Europe's current hydrogen demand, the country is committed to sustainability. The potential to triple this capacity using nuclear power demonstrates a willingness to explore diverse energy sources. With such initiatives, Oman is positioning itself as a key player in the global shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy solutions.
It is important to consider both the advantages and challenges associated with nuclear power while evaluating its role in the global energy transition. Likewise, Oman's vision for renewable energy presents an ambitious and promising approach that could significantly contribute to a more sustainable future.
Challenges The Idea is Addressing
Challenges of Nuclear Power: 1. Radioactive Waste Management: The proper handling and containment of radioactive waste are crucial to ensure safety during its decay process. The long-term management of nuclear waste remains a challenge, requiring secure storage and disposal facilities. 2. High Initial Costs: The construction of nuclear power plants involves high upfront capital costs, making it a considerable investment for countries exploring this energy option. 3. Safety Concerns: Nuclear power plants must adhere to strict safety protocols to prevent accidents and protect the environment and human health. The potential risks associated with nuclear accidents raise concerns among some communities. 4. Nuclear Proliferation: The technology used in nuclear power can potentially be diverted for nuclear weapons development, necessitating stringent safeguards and international cooperation to prevent proliferation. It is important to consider both the advantages and challenges associated with nuclear power while evaluating its role in the global energy transition. Likewise, Oman's vision for renewable energy presents an ambitious and promising approach that could significantly contribute to a more sustainable future.
Benefits of Idea Implementation
Advantages of Nuclear Power: 1. Reduced Carbon Pollution: Nuclear power generates virtually no carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, making it a low-carbon energy source. This has a significant impact on curbing climate change and reducing air pollution. 2. Massive Carbon Emission Avoidance: Nuclear energy has played a significant role in avoiding millions of tons of carbon pollution. This helps combat climate change and contributes to global efforts to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions. 3. Reliability: Nuclear power plants provide a reliable and stable source of energy, operating continuously regardless of weather conditions. This ensures a consistent power supply to meet energy demands. 4. Comparable GHG Emissions and Resource Use: Recent research suggests that nuclear power's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and resource use are similar to or even lower than those of renewable energy sources like solar and wind energy. Oman's Vision 2040 on Renewable Energy: 1. Ambitious Targets: Oman has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, particularly renewable hydrogen production. By aiming for significant annual hydrogen production capacities, Oman demonstrates its commitment to sustainable energy solutions. 2. Leadership in Sustainability: With its renewable energy vision, Oman positions itself as a leader in sustainable energy practices. This initiative showcases the country's dedication to environmental preservation and combatting climate change. 3. Diversification of Energy Sources: By considering the potential integration of nuclear power to triple renewable hydrogen production, Oman shows a willingness to explore diverse energy sources for a cleaner and more sustainable energy mix.
Team Members

Bio
Skills
Intrests
Resources

169081924636nuclear-power-round-logo-electricity-and-energy-industry-symbol-isolated-vector-image-700-262355650.jpg
Last Update:- 31 July 2023





 Winning Idea
Winning Idea 











